Equipment with multiple network interfaces
Every device that needs to communicate with the internet has one or more network interfaces. Each network interface has an identification called MAC Address . This identification is unique and each network interface has its own MAC Address, regardless of whether it is a wired interface or a wireless network interface.
When connecting a network interface to a switch or access point, if using automatic IP addressing (DHCP), this network interface will receive an IP Address that is linked to its MAC Address. In the DHCP server's view of the local network, an IP Address is not linked to a specific computer or smartphone, but rather is linked to a specific MAC Address.
This way, if you connect your notebook to the network via wireless connection (Wi-Fi), the wireless network interface will receive a certain IP Address. The moment you connect a network cable to connect to the local network via the cable, the wired network interface will receive another IP Address. In other words, your computer will be using 2 different IP addresses to connect to the same local network.
How to find out the MAC Address and IP Address of each network interface
- Press the Windows key (located next to the Alt key) and simultaneously press the Chat. This is the shortcut to open a box called To execute.

- In the Run box, type “cmd“and click OK.
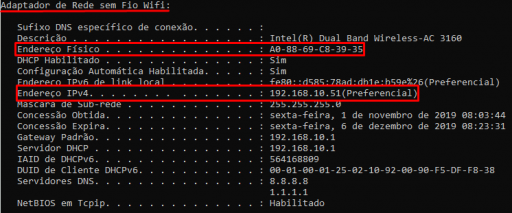
- In the Command Prompt window, type “ ipconfig /all ” and then press Enter.
- In the results of the “ipconfig /all” command, locate information about the “ Ethernet Adapter ” – this name may vary but normally contains the word Ethernet – this is the wired network interface. In this information there will be a line starting with “ Physical Address ”, which contains the MAC Address of this wired network interface and also a line with “ IPv4 Address ”, which contains the IP Address of the wired network interface.
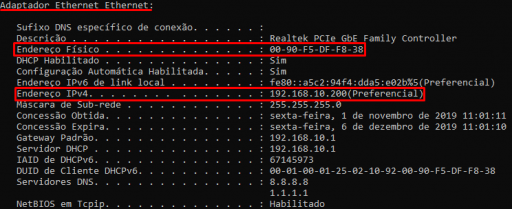
- Still in the “ipconfig /all” results, find a set of information about “ Wireless network adapter ” – this is the wireless network interface (wireless or Wi-Fi). In this block of information there will also be a line starting with “ Physical Address ”, which contains the MAC address of the wireless network interface; and a line starting with “ IPv4 Address “, which contains the IP Address of the wireless network interface.
Finding MAC Addresses and IP Addresses in the Lumiun Control Panel
If a notebook connected within the same hour via cable and also via Wi-Fi, 2 licenses will be counted: one for the IP Address of the wired interface and another for the IP Address of the Wi-Fi interface.
Lumiun counts each IP address being controlled and active in the last hour as a license in use.
Furthermore, it is technically possible to keep each of these IP addresses in different groups within the Lumiun control panel. If a certain computer normally accesses a website using the Wi-Fi network and cannot access that website via cable, this may be the explanation: the IP Address of the wired interface is in a group and the IP Address of the Wi-Fi interface is in another group.
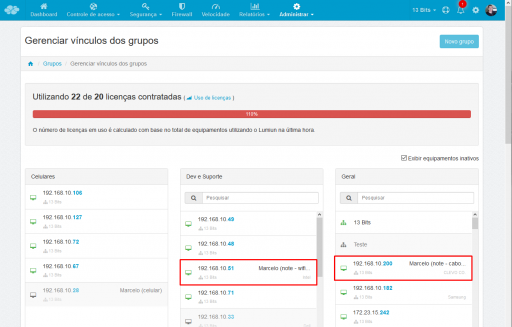
Look at the images below, let's check how Lumiun identified each of these network interfaces.
- In the Lumiun control panel, access the Manage > Equipment menu.
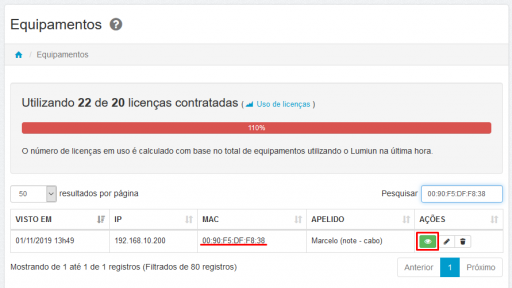
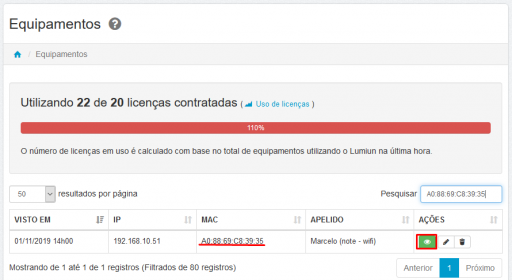
- Locate the MAC Addresses of the network interfaces and check the IP Addresses.
- Access the Manage > Groups menu. Check which group each of these IP addresses is in.
If you have any questions, please contact us and it will be a pleasure to assist you.